Elastic Beanstalk
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is an easy-to-use service for deploying and scaling web applications and services developed with Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, Go, and Docker on familiar servers such as Apache, Nginx, Passenger, and IIS.
To begin, simply upload your code and Elastic Beanstalk automatically handles the deployment, from capacity provisioning, load balancing, autoscaling to application health monitoring. At the same time, you retain full control over the AWS resources powering your application and can access the underlying resources at any time.
Elastic Beanstalk automatically provisions the resources required to run application deployment. AWS resources created for an environment include Route53 entry, an Elastic Load Balancer (ELB), an Auto Scaling Group (ASG), and one or more instances.
Once configured, the Beanstalk environment is highly dependent on its provisioned resources which are used for scaling and load balancing purposes.
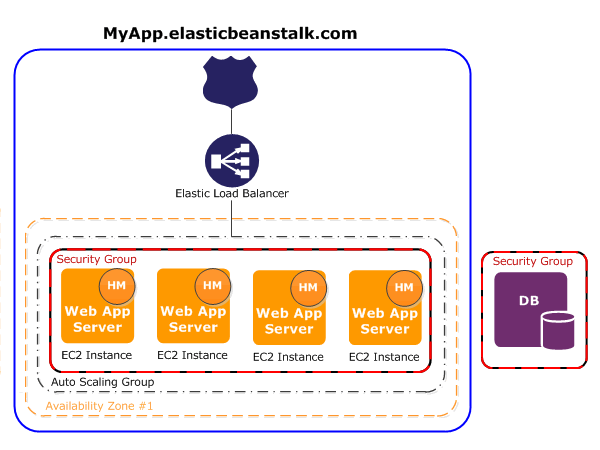
Due to the fact that the Elastic Beanstalk environment is dependent on its provisioned resources (such as CloudFormation, ELB, ASG), it is necessary to keep those in place and integrate only with the underlying ASG.
Elastic Beanstalk uses several strategies for rolling deployments: All at once, Rolling, Rolling with additional batch, Immutable.
Depending on the deployment policy configured in the Elastic Beanstalk environment, Elastigroup will identify it and use one of the following approaches to manage the cluster: in-ASG or independent Elastigroup.
| Elastic Beanstalk Deployment Policy | Spot Integration Method |
|---|---|
All at once | in-ASG |
Rolling | in-ASG |
Rolling with additional batch | Independent Elastigroup |
Immutable | Independent Elastigroup |
Single-instance environments will be integrated with Independent Elastigroup method, regardless of the deployment policy.
To learn more about Elastic Beanstalk deployment methods, see the following AWS documentation: Deployment Policies and Settings
Use a deployment policy that is supported by the in-ASG approach whenever possible.
Before starting, verify that the most up-to-date Spot IAM policy is configured in your AWS account.
The following sections explain how each integration mode works to help you better understand the concepts behind Elastigroup for Elastic Beanstalk as well as debugging in case of a potential failure in the setup and scale process.
- In-ASG integration. This is the recommended approach whenever possible.
- Independent Elastigroup integration.