Ocean for Apache Spark
Ocean for Apache Spark (also referred to in the user documentation as Ocean Spark) is a managed cloud-native Spark platform that can be deployed in your cloud account. As of December 2021, Ocean Spark is available on AWS, Azure, and GCP, and is an alternative to managed services like Databricks, EMR, Google Dataproc, Azure HDInsight, or DIY Spark infrastructures.
Running on top of Ocean, Spot's serverless infrastructure engine for containers, Ocean Spark makes it easy for your data teams to be successful with Apache Spark on Kubernetes, without dealing with the complexity of managing servers.
Ocean Spark features intuitive UIs from which you can view your applications configurations, logs, key metrics, Spark UI, and costs. It provides reliable, automated, and continuously optimized cloud infrastructure and Spark configurations, resulting in significant time and cost savings.
Key Features
Ocean Spark makes it easy to provision, configure, and monitor Kubernetes clusters in your cloud account, and then run containerized Spark applications on top of it. Here are some of the key features.
Spark-Centric Observability Layer
Like with any Ocean cluster, the Spot console gives you visibility over your Kubernetes cluster(s): nodes, pods, scaling activity, costs at the cluster-level.
With Ocean for Spark, a unique Spark-centric observability layer is added, giving you visibility over your Spark applications' configurations, logs, Spark UI, and key metrics (CPU, Memory, I/O, Spark efficiency ratio, Shuffle). This information is available both while the app is running and after it is completed.
Spark Jobs Configuration Optimization
A job is a set of Spark applications — typically the same application code that you run regularly. Since the ID of a job is a required field when you submit a Spark application through our API, you explicitly define the grouping of applications in jobs.
Ocean Spark automatically tunes certain infrastructure parameters (e.g., container sizes, # of executors) and Spark configurations (e.g., I/O optimization, memory management, shuffle, Spark feature flags) based on past execution of your Spark jobs.
You can track the evolution of each of your job's performance, stability, costs, and other key metrics in a dedicated dashboard.
Automatically Scaled and Optimized Infrastructure
Leveraging advanced AI algorithms, Ocean Spark automatically scales your cluster(s) based on the real-time load, choosing the highest-performance, lowest-cost instances (including spot nodes) matching your workload requirements.
The scheduling of pods (containers) onto nodes (instances) is optimized with a bin-packing algorithm to maximize efficiency and reduce your costs. An automatic headroom can be configured to guarantee that your Spark applications can start instantaneously without waiting for new capacity to be provisioned.
External Integrations
Ocean for Spark includes pre-built integrations with Jupyter notebooks (Jupyter Enterprise Gateway) and popular scheduling tools like Airflow. Our REST API lets you securely submit Spark applications from anywhere. In addition, Spark can be configured to read/write data to all popular data storages, as well as to use external Hive metastore.
The open and flexible architecture of Ocean lets you leverage popular cloud-native technologies in networking, security, observability, and CI/CD.
Fleet of Spark Docker Images to Build Upon
The Ocean for Spark team maintains a fleet of optimized Docker images for Apache. These images contain the Spark distribution itself (Spark 2.4 and later) as well as popular connectors for data sources (S3, GCS, ADLS, Snowflake, Delta Lake, Kafka, and more) as well as Scala, Java, Python, and Hadoop.
You can use these images directly, or choose to build your own custom Docker images on top of them. You can run these images locally, or at scale on the Kubernetes cluster, and benefit from a reliable and fast developer workflow.
Architecture Overview
The diagram below shows an architectural overview of Ocean Spark.
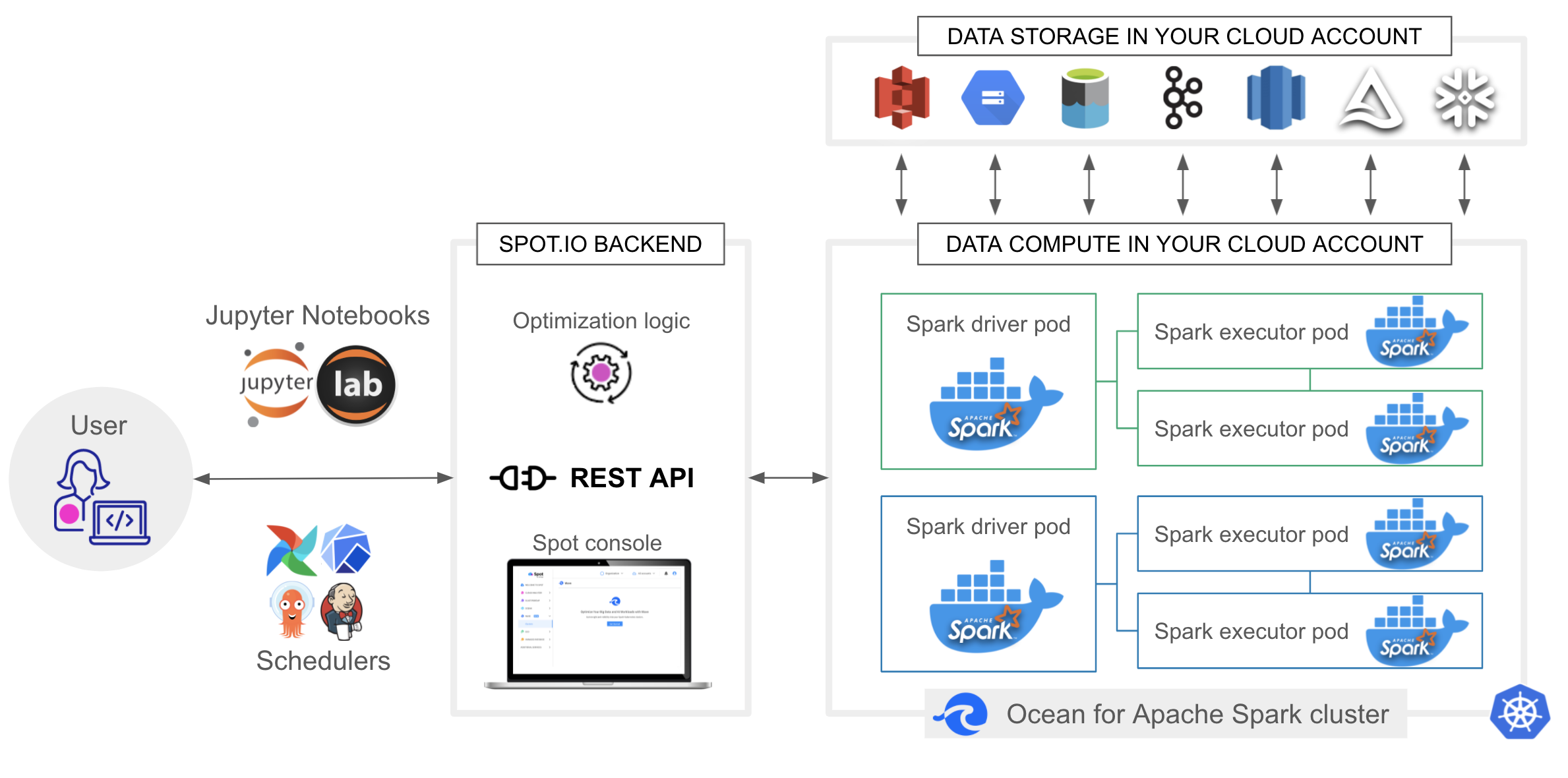
End Users
You can start interactive Spark sessions by connecting Jupyter notebooks (Jupyter, JupyterLab, JupyterHub), or submit batch or streaming applications through the REST API. We provide integrations with popular schedulers such as Airflow, but it's also easy to implement to your own custom workflow orchestrator. They can then track the execution of their Spark applications by logging in to the Spot console.
Spot.io Control Plane (Backend)
The Spot console, the REST API, and the Kubernetes and Spark optimization logic are hosted in the Spot.io control plane. These services continuously monitor your Ocean for Spark cluster(s) to enable the key features such as the management, monitoring, and optimization of your cluster and Spark applications.
Ocean Spark Cluster
The Ocean Spark cluster itself is a Kubernetes cluster in your cloud account. This is where the Spark applications are running inside pods, Docker containers. You can run hundreds of Spark applications in parallel, using a variety of Spark versions and dependencies (each Spark application is fully isolated and independent), on a heterogeneous infrastructure made of an optimized mix of different instances (instance family, instance size, spot or on-demand).
Data Sources
Spark can read data from (and write data to) a wide range of data sources and formats including object stores, data warehouses, streaming sources, relational and non-relational databases.
You can leverage cloud security best-practices (such as IAM role and Kubernetes secrets) to give your Spark applications permission to access the data in the most secure manner. The sensitive data Spark works with stays protected in your cloud account all the time.
What's Next?
- If you are new to Spot, connect your cloud provider to Spot.
- If you are already a Spot user, go ahead and Get Started with Ocean Spark.